Universitwafer: 45 results found.
 |
Semiconductor Wafer Bonding
Wafer bonding is a method used in semiconductor manufacturing by silicon on insulator (SOI) technology. In wafer bonding the insulating layer is formed by directly bonding oxidized silicon with a second substrate. The majority of the second substrate is subsequently removed, the remnants forming the topmost Si layer.
Semiconductorwaferbonding.com ~
Site Info
Whois
Trace Route
RBL Check
|
 |
SiO2 Wafer
The chemical compound silicon dioxide, also known as silica (from the Latin silex), is an oxide of silicon with a chemical formula of SiO2 and has been known for its hardness since antiquity. Thin films of silica grown on silicon wafers via thermal oxidation methods can be quite beneficial in microelectronics, where they act as electric insulators with high chemical stability. In electrical applications, it can protect the silicon, store charge, block current, and even act as a controlled pathway to limit current flow.
Sio2wafer.com ~
Site Info
Whois
Trace Route
RBL Check
Similar Sites:
thermaloxide.com
|
 |
Semiconductor Processing
Semiconductor device processing is used to create the integrated circuits (silicon chips) that are present in everyday electrical and electronic devices. It is a multiple-step sequence of photographic and chemical processing steps during which electronic circuits are gradually created on a wafer made of pure semiconducting material.
Semiconductorprocessing.net ~
Site Info
Whois
Trace Route
RBL Check
Similar Sites:
semiconductorprocessing.org
|
 |
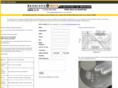
Silicon Manufacture
The current industrial production of silicon is via the reaction between carbon (charcoal) and silica at a temperature around 1700 °C. In this process, known as carbothermic reduction, each tonne of silicon (metallurgical grade, about 98% pure) is produced with the emission of about 1.5 tonnes of carbon dioxide.
Siliconmanufacture.com ~
Site Info
Whois
Trace Route
RBL Check
|
 |
Silicon Processing
The current industrial production of silicon is via the reaction between carbon (charcoal) and silica at a temperature around 1700 °C. In this process, known as carbothermic reduction, each tonne of silicon (metallurgical grade, about 98% pure) is produced with the emission of about 1.5 tonnes of carbon dioxide.
Siliconprocessing.org ~
Site Info
Whois
Trace Route
RBL Check
|
 |
Single Crystal Quartz
A single crystal solid is a material in which the crystal lattice of the entire sample is continuous and unbroken to the edges of the sample, with no grain boundaries. Because grain boundaries can have significant effects on the physical and electrical properties of a material, single crystals are of interest to industry, and have important industrial applications.
Singlecrystalquartz.com ~
Site Info
Whois
Trace Route
RBL Check
|
|
|
|